Navigating roundabouts in the UAE can be challenging for both new residents and experienced drivers, especially with varying interpretations of the rules. Understanding UAE roundabout rules is essential for safe driving, avoiding fines, and preventing accidents. This comprehensive guide explains everything from basic right-of-way principles to advanced maneuvering techniques, ensuring you can navigate any roundabout in the UAE with confidence.
Why Roundabout Rules Matter in the UAE
The UAE Roundabout Landscape:
- Historical Infrastructure: Many roundabouts were built before current traffic volumes
- International Driver Mix: Over 200 nationalities with different roundabout experiences
- Serious Consequences: Accidents at roundabouts often cause significant damage and injuries
- Substantial Fines: Violations can result in fines up to 1,000 AED and black points
Common Problems at UAE Roundabouts:
- Confusion about right-of-way (most common issue)
- Incorrect lane usage (cutting across lanes)
- Failure to signal (especially when exiting)
- Last-minute decisions causing dangerous maneuvers
- Speed mismanagement (too fast or too slow)
The Foundation: Official UAE Traffic Law Roundabout Rules
Federal Traffic Law Articles:
Article 69: Priority Rule
“Vehicles within the roundabout have the right-of-way over vehicles entering the roundabout.”
This is the golden rule: Vehicles already circulating in the roundabout always have priority. This applies regardless of which lane they’re in or where they entered from.
Article 71: Lane Discipline
“Drivers must maintain their lane within the roundabout and may only change lanes when safe and after signaling.”
Article 73: Exit Procedure
“Drivers must use appropriate indicators when exiting the roundabout.”
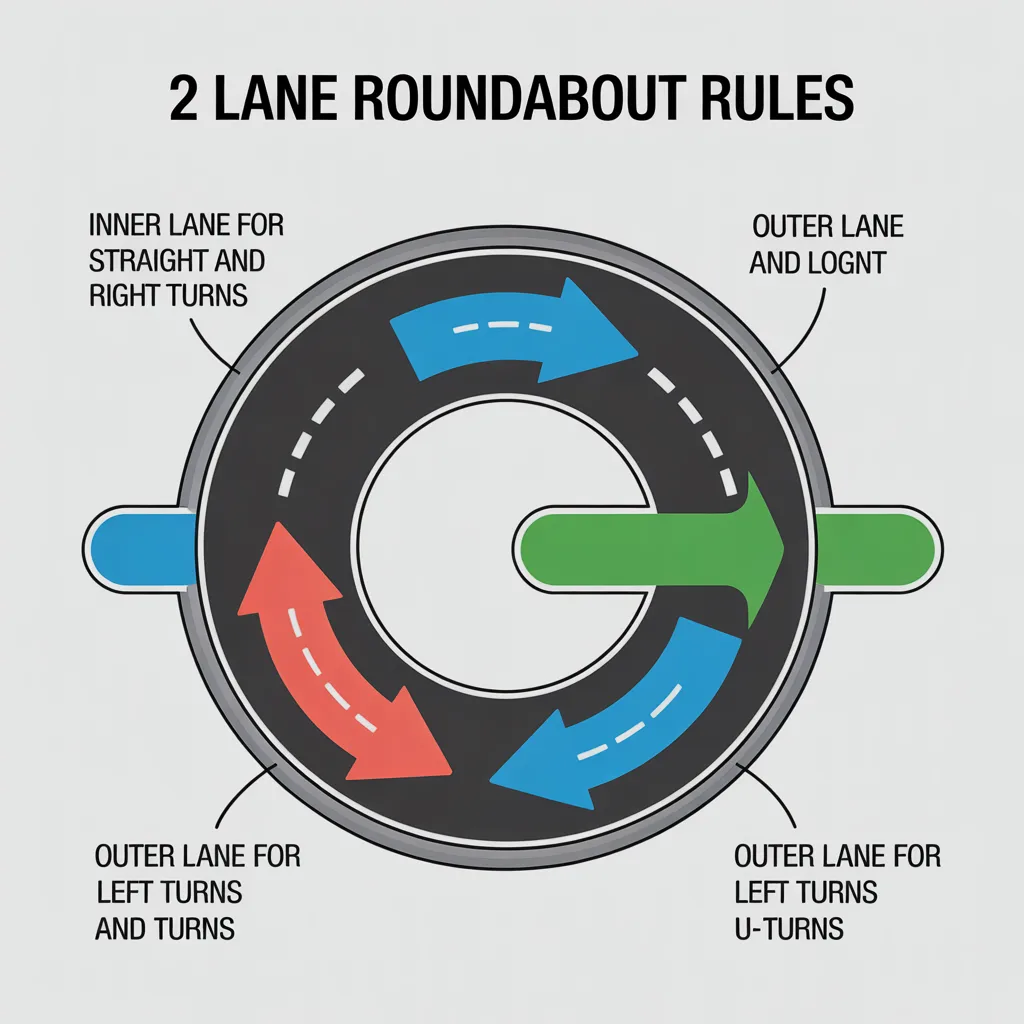
The Four Essential Steps for Every Roundabout
Step 1: Approach and Lane Selection
Choose your lane BEFORE entering based on your intended exit.
| Your Intended Exit | Correct Approach Lane | Signaling on Approach |
|---|---|---|
| First exit (right turn) | Right lane | Right indicator |
| Second exit (straight ahead) | Right or middle lane | No signal |
| Third exit (left turn) | Left lane | Left indicator (optional) |
| U-turn (fourth or later exit) | Left lane | Left indicator (optional) |
Important Exception: Some larger roundabouts have lane markings on approach – ALWAYS follow these markings as they override general rules.
Step 2: Entering the Roundabout
Yield to ALL vehicles already in the roundabout.
Common Mistake: Drivers only check the lane immediately to their left. You must check ALL lanes because vehicles may be changing lanes within the roundabout.
Correct Procedure:
- Approach at reduced speed (typically 20-40 km/h)
- Check all circulating lanes (left, ahead, right)
- Look for gaps in traffic, not just the closest lane
- Wait if necessary – never force your way in
- Enter only when safe
Step 3: Navigating Within the Roundabout
Maintain lane discipline and appropriate speed.
Key Rules:
- Stay in your chosen lane until preparing to exit
- Maintain consistent speed (don’t stop unless necessary)
- No overtaking within the roundabout
- Keep safe distance from vehicle ahead
Signaling Inside Roundabout:
- No signal while circulating (unless changing lanes)
- Right signal ONLY when approaching your exit
- Signal timing: Start signaling approximately at the exit BEFORE yours
Step 4: Exiting Safely
Exit correctly and signal your intention.
Proper Exit Technique:
- Check mirrors and blind spot before exiting
- Signal right approximately 30 meters before exit
- Exit to appropriate lane (right lane to right lane, etc.)
- Cancel signal after exiting
- Accelerate smoothly to match traffic flow
Understanding UAE Roundabout Types
Standard Single-Lane Roundabouts:
Most common in residential areas
Rules:
- Simple to navigate
- Yield to circulating traffic
- Signal right when exiting
- Maximum speed: 20-30 km/h
Multi-Lane Roundabouts:
Common on major roads
Rules:
- Follow lane markings strictly
- Choose lane based on intended exit
- No lane changing in circle unless absolutely necessary
- Be aware of larger vehicles needing more space
Signalized Roundabouts:
Roundabouts with traffic lights
Rules:
- Traffic lights override normal roundabout rules
- Stop on red even if roundabout appears clear
- Proceed on green while still yielding to circulating traffic if applicable
- Common in Abu Dhabi and Sharjah
Turbo Roundabouts (Increasingly Common):
Designed to prevent lane weaving
Features:
- Physical lane dividers
- Forces you to choose correct lane before entering
- Follow painted lane markings exactly
- No lane changing possible within roundabout
Mini-Roundabouts:
Small circles at intersections
Rules:
- Treat as standard roundabouts
- Often found in communities and compounds
- Be extra cautious due to limited visibility
- Large vehicles may need to drive over the center
Right-of-Way Hierarchy at UAE Roundabouts
Priority Order:
- Vehicles already circulating in the roundabout (highest priority)
- Emergency vehicles with lights/sirens (yield immediately)
- Public transportation buses (in some cases, depending on local rules)
- Vehicles entering the roundabout (lowest priority)
Special Considerations:
- Large vehicles (trucks, buses) may need more space – be patient
- Oversized vehicles may take multiple lanes – keep clear
- Motorcycles can be harder to see – double check
- Cyclists may use roundabouts differently – give them space
Signaling: The Language of Roundabouts
Correct Signaling Protocol:
When Entering:
- Turning right (first exit): Signal right on approach
- Going straight: No signal on approach
- Turning left or U-turn: Signal left on approach (optional in UAE)
While Circulating:
- No signal while in the roundabout
- Exception: If changing lanes within roundabout (not recommended)
When Exiting:
- Signal right approximately at the exit before yours
- Continue signal until completely exited
- Cancel signal after exit
Common Signaling Mistakes:
- Signaling left while circulating (confuses other drivers)
- Not signaling when exiting (major cause of accidents)
- Signaling too early or too late (causes confusion)
- Forgetting to cancel signal after exiting
Speed Management at Roundabouts
Approaching Speed:
- Standard roundabouts: Reduce to 20-40 km/h
- Large roundabouts: 30-50 km/h may be appropriate
- Always adjust for conditions (rain, fog, traffic)
Circulating Speed:
- Maintain consistent speed (don’t accelerate aggressively)
- Be prepared to stop if someone cuts you off
- Match speed with circulating traffic
Exiting Speed:
- Accelerate smoothly after exiting
- Check speed limit of exiting road
- Don’t accelerate while still in the roundabout
Special Vehicles and Roundabouts
Large Vehicles (Trucks, Buses):
- May need multiple lanes to turn
- Often swing wide on entry and exit
- Be patient and give them space
- Never squeeze beside them in a roundabout
Motorcycles and Scooters:
- Harder to see – check twice
- May filter between lanes (legality varies)
- Give them extra space
- Be aware they may be in your blind spot
Emergency Vehicles:
- If approaching with lights/sirens: Clear the roundabout if possible
- If already in roundabout: Continue and exit normally, then pull over
- Never stop in the middle of a roundabout
- Do not block exits for emergency vehicles
Bicycles:
- Increasingly common in some areas
- May use bicycle lanes around roundabouts
- Give them space – they’re vulnerable road users
- Be extra cautious in communities with bike paths
Common Roundabout Violations and Penalties
Fine Structure (Federal Traffic Law):
| Violation | Fine (AED) | Black Points | Vehicle Impound |
|---|---|---|---|
| Failure to yield to circulating traffic | 500 | 4 | No |
| Incorrect lane usage in roundabout | 400 | 0 | No |
| Failure to signal when exiting | 300 | 0 | No |
| Changing lanes within roundabout | 400 | 0 | No |
| Stopping inside roundabout (except traffic) | 500 | 0 | No |
| Driving against flow of traffic | 1,000 | 12 | 30 days |
| Endangering others | 1,000 | 6 | 7 days |
Additional Consequences:
- Increased insurance premiums after violations
- License suspension with multiple offenses
- Possible deportation for serious offenses by visitors
- Civil liability for accidents caused
Defensive Driving Techniques for Roundabouts
The SEE System (Search, Evaluate, Execute):
Search:
- Scan all approaching roads
- Check mirrors every 5-8 seconds
- Look for vehicles, pedestrians, obstacles
- Identify potential hazards early
Evaluate:
- Assess speed of circulating traffic
- Identify gaps in traffic
- Consider other drivers’ possible actions
- Plan your path through the roundabout
Execute:
- Execute your plan smoothly
- Maintain lane discipline
- Signal intentions clearly
- Adjust as needed for changing conditions
Space Cushion Technique:
- Maintain buffer around your vehicle
- Increase following distance in roundabouts
- Position vehicle to maximize visibility
- Have escape routes in mind
Eye Contact and Communication:
- Make eye contact with other drivers when possible
- Use signals clearly and timely
- Position vehicle to communicate intentions
- Be predictable in your actions
Pedestrian Crossings at Roundabouts
Rules for Drivers:
- Yield to pedestrians at marked crossings
- Stop before the white line at pedestrian crossings
- Do not block the crossing when waiting
- Be extra cautious during school hours
Rules for Pedestrians:
- Use designated crossings when available
- Make eye contact with drivers
- Wait for clear gap in traffic
- Don’t assume drivers see you
Special Considerations:
- School zones: Increased pedestrian activity
- Shopping areas: Higher pedestrian volumes
- Residential areas: Children and pets may dart out
- Tourist areas: Pedestrians may be unfamiliar with local rules
Weather and Visibility Considerations
Rainy Conditions:
- Reduce speed significantly
- Increase following distance
- Use headlights (not just parking lights)
- Be prepared for hydroplaning
Fog and Reduced Visibility:
- Use fog lights if visibility below 100m
- Reduce speed to match visibility
- Increase following distance
- Listen for other vehicles
Night Driving:
- Ensure lights are working properly
- Reduce speed slightly
- Watch for unlit vehicles
- Be aware of glare from other vehicles’ lights
Sandstorms:
- Pull over safely if visibility becomes dangerous
- Use hazard lights if moving slowly
- Keep windows closed
- Clean windshield before entering roundabout
Roundabout Accidents: Prevention and Procedure
Common Accident Scenarios:
- Side-impact collisions from failure to yield
- Rear-end collisions from sudden stopping
- Sideswipe collisions from lane changing
- Pedestrian accidents at crossings
Accident Prevention Tips:
- Never assume other drivers know the rules
- Be extra cautious during peak traffic times
- Watch for distracted drivers
- Avoid roundabouts if you’re unsure or nervous
If Involved in an Accident:
- Move to safety if vehicles are drivable
- Call police (999) if injuries or significant damage
- Exchange information with other driver(s)
- Document the scene (photos, witness information)
- Contact insurance company
- Do not admit fault at the scene
Technology and Roundabout Navigation
Useful Apps and Tools:
- Google Maps/Waze: Shows roundabout layouts and lanes
- UAE Traffic Apps: Dubai Police, Abu Dhabi Police apps
- Dashcams: Provide evidence in case of disputes
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): Some systems detect roundabouts
Vehicle Technology:
- Blind spot monitoring: Helps with lane changes
- Rear cross-traffic alert: Useful when exiting
- 360-degree cameras: Help with spatial awareness
- Heads-up displays: Keep eyes on road
Emirate-Specific Roundabout Variations
Dubai:
- Generally follows federal rules strictly
- Heavy enforcement in certain areas
- Many roundabouts converted to signalized intersections
- Smart roundabouts with adaptive technology
Abu Dhabi:
- More signalized roundabouts
- Strict enforcement of lane discipline
- Higher fines for certain violations
- Advanced traffic management systems
Sharjah:
- Mixed roundabout types
- Often congested – extra patience needed
- Pedestrian-heavy roundabouts
- School zones with special restrictions
Northern Emirates:
- Varying enforcement levels
- Mix of modern and older roundabouts
- Less congestion typically
- Different driver behavior patterns
Roundabout Practice Locations
For Beginners:
- Residential community roundabouts (low traffic)
- Industrial area roundabouts (off-peak hours)
- University/school area roundabouts (during holidays)
For Intermediate Practice:
- Two-lane roundabouts in suburban areas
- Signalized roundabouts during off-peak
- Roundabouts with pedestrian crossings
For Advanced Mastery:
- Multi-lane roundabouts during moderate traffic
- Complex intersections with multiple roundabouts
- High-speed approach roundabouts
Future of Roundabouts in the UAE
Development Trends:
- Conversion to signals: Many roundabouts being replaced
- Smart roundabouts: Adaptive traffic control systems
- Improved signage: Better lane guidance and warnings
- Pedestrian safety enhancements: Better crossings and signals
Technology Integration:
- AI traffic management: Optimizing roundabout flow
- Connected vehicle systems: Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication
- Automated enforcement: More consistent violation detection
- Real-time information: Dynamic signage and app notifications
Your Personal Roundabout Improvement Plan
Week 1: Knowledge Building
- Study the right-of-way rules until automatic
- Understand lane selection principles
- Learn signaling requirements
- Review local emirate variations
Week 2: Observation Practice
- Be a passenger and observe other drivers
- Note common mistakes and near-misses
- Practice predicting other drivers’ actions
- Identify challenging roundabouts in your area
Week 3: Controlled Practice
- Practice at quiet roundabouts early mornings
- Focus on one skill at a time (entry timing, lane discipline, exiting)
- Get feedback from experienced drivers
- Record your progress
Week 4: Real-World Application
- Navigate your regular routes confidently
- Handle peak traffic roundabouts
- Manage complex multi-lane roundabouts
- Teach others the correct rules
Ongoing: Continuous Improvement
- Stay updated on rule changes
- Adapt to different roundabout designs
- Maintain defensive driving habits
- Share knowledge with family and friends
Roundabout Rules for Specific Situations
During Ramadan:
- Increased traffic before iftar
- Potentially tired drivers – be extra cautious
- Different traffic patterns – allow extra time
- Respect cultural considerations
During Eid and Holidays:
- Heavy traffic around malls and attractions
- Visitors unfamiliar with local roundabouts
- Increased pedestrian activity
- Allow extra time for journeys
During Events:
- Road closures may affect roundabout access
- Changed traffic patterns
- Increased tourist drivers
- Follow temporary signage
With Rental Cars:
- Familiarize yourself with vehicle size and handling
- Check insurance coverage for roundabout accidents
- Be extra cautious if unfamiliar with UAE rules
- Ask rental company for local roundabout tips
Psychological Aspects of Roundabout Navigation
Managing Anxiety:
- Start small with simple roundabouts
- Practice during low-traffic times
- Use positive self-talk
- Remember that confidence comes with practice
Dealing with Aggressive Drivers:
- Don’t escalate confrontations
- Maintain your position (don’t be bullied)
- Report dangerous behavior if safe to do so
- Focus on your own safe driving
Building Confidence:
- Celebrate small successes
- Track your progress
- Get professional instruction if needed
- Remember that even experienced drivers make mistakes
Environmental Benefits of Proper Roundabout Use
Efficiency Gains:
- Reduced idling compared to traffic lights
- Smoother traffic flow
- Lower fuel consumption
- Reduced emissions
Safety Benefits:
- Fewer severe collisions (roundabouts reduce high-speed impacts)
- Lower pedestrian accident rates (when properly designed)
- Reduced conflict points compared to intersections
Community Benefits:
- Quieter neighborhoods (less stopping and starting)
- Lower maintenance costs than signalized intersections
- Enhanced aesthetics with landscaping opportunities
Conclusion: Mastering UAE Roundabouts
Understanding and properly applying UAE roundabout rules is essential for safe, efficient driving. While roundabouts can seem intimidating at first, they become straightforward with knowledge and practice.
Key Principles to Remember:
- Yield to circulating traffic – always
- Choose your lane before entering – based on your exit
- Signal when exiting – right signal before your exit
- Maintain lane discipline – no cutting across lanes
- Be predictable – other drivers should be able to anticipate your actions
Final Advice:
Roundabouts are designed to keep traffic moving safely. When everyone follows the rules, they work efficiently. Be patient with yourself as you learn, and be patient with others who may still be learning. Defensive driving – anticipating others’ mistakes while avoiding your own – is the best approach to roundabout navigation in the UAE.
Whether you’re a new resident, a visitor, or a long-time driver refreshing your knowledge, mastering roundabout rules will make your driving experience in the UAE safer, less stressful, and more enjoyable.