Navigating roundabouts in Dubai can be one of the most confusing aspects of driving in the emirate for both new residents and experienced visitors. With over 100 major roundabouts throughout the city—each with its own unique flow patterns, signage, and unwritten rules—understanding Dubai roundabout rules is essential for safe, efficient, and fine-free driving. This comprehensive guide will transform you from a hesitant roundabout navigator into a confident, rule-abiding driver who moves through Dubai’s circular intersections with ease.
Why Dubai’s Roundabouts Demand Special Attention
Before we dive into the rules, let’s understand why roundabouts in Dubai present unique challenges:
The Dubai Roundabout Landscape
- Historical Design: Many roundabouts were built before population explosion, now handling 5-10x intended traffic
- Cultural Mix: Drivers from 200+ nationalities with different roundabout experiences
- Infrastructure Evolution: Some roundabouts function more like signalized intersections
- Penalty System: High fines (up to 1,000 AED) for incorrect roundabout navigation
The Psychological Factor
Research shows that 68% of drivers experience increased stress at Dubai roundabouts due to:
- Uncertainty about right-of-way
- Aggressive driving behaviors
- Last-minute lane changes
- Unpredictable pedestrian movements
The Foundation: UAE Federal Traffic Law Roundabout Rules
The official rules provide the legal framework:
Article 69: Right-of-Way Priority
“Vehicles within the roundabout have the right of way over vehicles entering the roundabout.”
This single sentence is the most important—and most violated—rule. Yet it’s only the beginning of understanding proper roundabout navigation.
Article 71: Lane Discipline
“Drivers must maintain their lane within the roundabout and may only change lanes when safe and after signaling.”
Article 73: Exit Protocol
“Drivers must use the appropriate indicator when exiting the roundabout.”
The Practical Application: How Dubai Roundabouts Actually Work
The Four Critical Steps for Every Roundabout
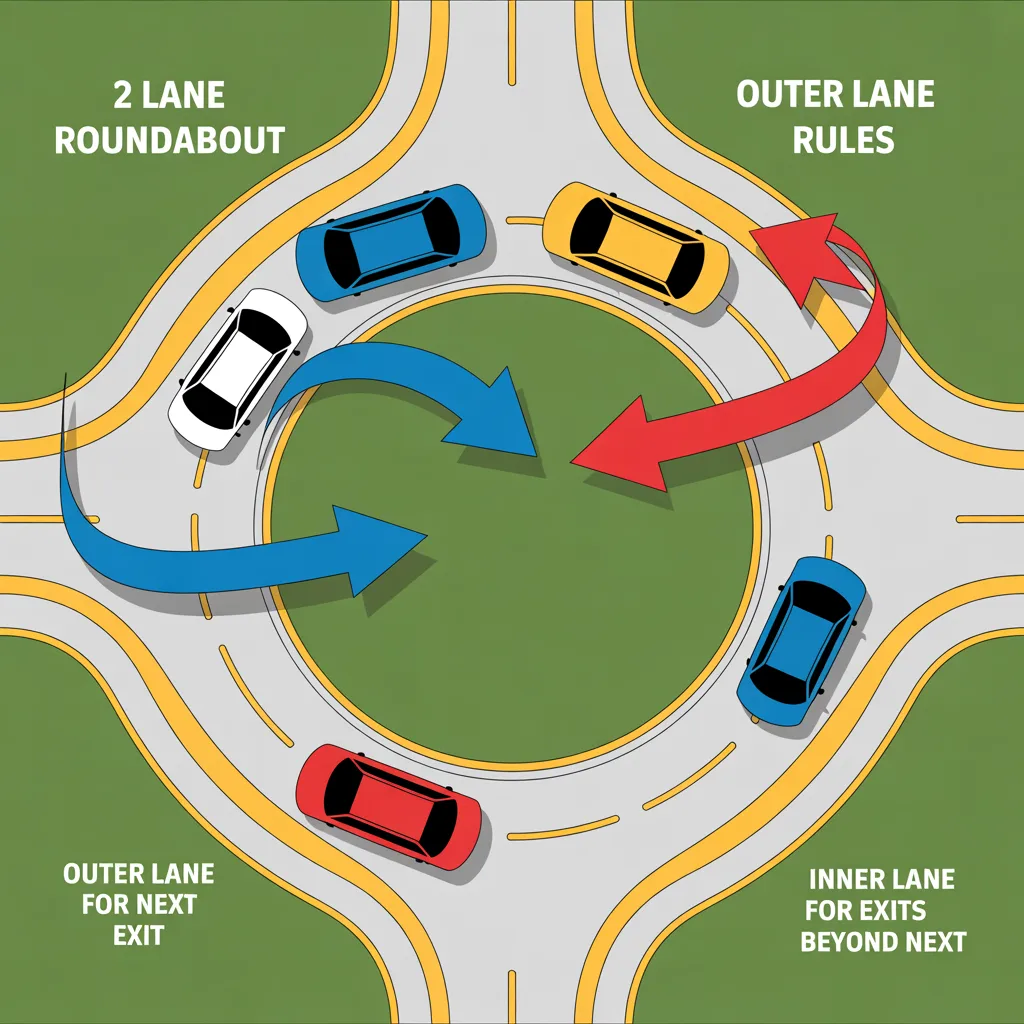
Step 1: Approach and Lane Selection
Rule: Choose your lane BEFORE entering based on your intended exit.
| Your Intended Exit | Correct Approach Lane |
|---|---|
| First exit (right turn) | Right lane |
| Second exit (straight ahead) | Middle or right lane (depending on roundabout size) |
| Third exit (left turn) or U-turn | Left lane |
Dubai Reality Check: Many drivers ignore this, causing dangerous weaving. Always check signage—some roundabouts have dedicated lanes marked on approach.
Step 2: Entry Timing and Yielding
Rule: Yield to ALL vehicles already IN the roundabout, not just those immediately to your left.
Common Mistake: Drivers only check for vehicles in the lane closest to them. You must check ALL lanes since vehicles may be changing lanes within the roundabout.
Pro Technique: Use the “two-second gap” rule. If a vehicle passes your entry point, wait two seconds before entering to ensure safe following distance.
Step 3: Navigation Within the Roundabout
Rule: Maintain your lane position and speed (typically 20-40 km/h depending on roundabout size).
Lane Discipline Challenges:
- Small Roundabouts: Often single-lane, easier navigation
- Medium Roundabouts (2-3 lanes): Require strict lane discipline
- Large Roundabouts (4+ lanes, like Defense Roundabout): Function like multiple intersections
Signal Usage INSIDE Roundabout:
- No signal while circulating (contrary to some drivers’ practice)
- Right signal ONLY when approaching your exit
- Signal for approximately 30 meters before exit
Step 4: Exiting Safely
Rule: Exit from the appropriate lane corresponding to your approach lane.
Exit Lane Alignment:
- If you entered from right lane, exit to right lane
- If you entered from left lane, check mirrors and blind spot before exiting to left lane
- Never cut across multiple lanes to exit
Special Roundabout Types in Dubai
Signal-Controlled Roundabouts
Some major roundabouts now have traffic lights:
- Al Barsha Roundabout: Partial signal control during peak hours
- Mamzar Roundabout: Full signalization
- Rule Adaptation: When lights are operational, they override normal roundabout rules
Turbo Roundabouts
Designed to prevent lane weaving:
- Example: Sheikh Zayed Road entry points
- Design: Physical lane separators that guide you to correct exit
- Key Rule: Once in your lane, you cannot change lanes until exit
Mini-Roundabouts
Common in residential areas:
- Rule: Treat exactly like larger roundabouts
- Challenge: Often have limited visibility
- Speed: Maximum 20 km/h recommended
Multi-Level Roundabouts
Some function as complex interchanges:
- Example: Trade Centre Roundabout (now largely reconfigured)
- Strategy: Study layout before approaching, follow signage meticulously
The Most Problematic Dubai Roundabouts & How to Conquer Them
1. Defense Roundabout (Al Dhiyafa Road)
The Challenge: 5 exits, 4 lanes, constant heavy traffic
Strategy:
- Approach in lane corresponding to exit number
- Be prepared for sudden lane changers
- Consider alternative routes during peak hours
Exit Mapping: - Exit 1 (Beach Road): Right lane
- Exit 3 (Jumeirah Road): Second from right
- Exit 5 (Al Wasl Road): Second from left or left lane
2. Mirdif City Centre Roundabout
The Challenge: Shopping traffic combined with residential flow
Strategy:
- Extreme patience during weekends (Thursday-Friday)
- Watch for pedestrians crossing illegally
- Use mall parking entrances/exits carefully
3. Al Khail Road Roundabouts
The Challenge: High-speed approaches with sudden congestion
Strategy:
- Reduce speed gradually from 100 km/h to 40 km/h
- Use indicators earlier than normal
- Be aware of trucks/buses with wider turning radius
4. Academic City Roundabouts
The Challenge: Student drivers and frequent new residents
Strategy:
- Increased following distance
- Assume other drivers might hesitate or make errors
- Extra caution during semester start/end dates
Pedestrian Crossings at Roundabouts: The Overlooked Rule
Official Regulations:
- Pedestrians have right-of-way at marked crossings
- Drivers must stop before the white line
- No stopping ON the crossing
Dubai Reality:
- Many pedestrians cross at unmarked locations
- Some roundabouts have overhead pedestrian bridges (use them!)
- During Ramadan evenings, pedestrian activity increases significantly
Safe Practice:
- Scan for pedestrians approaching crossings
- Be prepared to stop even if pedestrian is still on sidewalk
- Never block the crossing when waiting to enter roundabout
Roundabout Fines and Penalties: What Can Go Wrong
Understanding penalties reinforces good habits:
Common Roundabout Violations and Fines:
| Violation | Fine (AED) | Black Points | Vehicle Impound |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entering without yielding | 500 | 4 | No |
| Wrong lane usage | 400 | – | No |
| Exiting without signaling | 300 | – | No |
| Cutting across lanes inside | 400 | – | No |
| Stopping inside roundabout (except traffic) | 500 | – | No |
| Driving against flow | 1,000 | 12 | 30 days |
| Pedestrian right-of-way violation | 500 | 6 | No |
The “Minor” Violation That Isn’t Minor:
Failure to yield causes approximately 23% of roundabout accidents in Dubai. The 500 AED fine is often the least concern—repair costs and insurance premium increases are far more costly.
Roundabout Etiquette: The Unwritten Rules
Communication Through Indicators:
- Intent to enter: No signal needed (some drivers flash headlights, but this isn’t standard)
- Circulating: No signal
- Exiting: Right indicator 30m before exit
- Lane change within roundabout: Signal intention, check mirrors and blind spot
Eye Contact and Awareness:
- Make brief eye contact with drivers at entry points when possible
- Watch front wheels of waiting vehicles (they indicate intention to move)
- Monitor motorcycles and bicycles—they’re harder to see
Dealing with Aggressive Drivers:
- Don’t escalate: Let them pass if they’re tailgating
- Maintain position: Don’t be bullied out of your lane
- Report dangerous behavior: Use Dubai Police app if safe to do so
Weather and Visibility Considerations
Rain and Roundabouts:
- Reduced traction: Increase following distance by 50%
- Poor visibility: Use headlights, not just parking lights
- Flooding: Some roundabouts collect water—proceed slowly to avoid hydroplaning
Fog and Sandstorms:
- Use fog lights if visibility below 100m
- Reduce speed significantly
- Hazard lights only if stopped or moving very slowly
Night Driving:
- Approach carefully: Depth perception decreases
- Watch for unlit vehicles: Some older trucks have poor lighting
- Glare management: Don’t look directly at approaching headlights
Roundabout Improvements and Future Developments
Smart Roundabout Technology:
- Adaptive traffic signals: Adjust timing based on real-time flow
- AI monitoring: Detects congestion and accidents
- Digital signage: Provides lane guidance and warnings
Roundabout Removal/Replacement:
Many traditional roundabouts are being replaced with:
- Signalized intersections (e.g., former Clock Tower Roundabout)
- Interchanges (e.g., Garn Al Sabkha intersection)
- Tunnels and flyovers
Current Major Projects:
- Al Yasmeen Roundabout improvements: Adding dedicated turning lanes
- Academic City roundabout optimization: Better signage and lane markings
- DIP (Dubai Investment Park) roundabout upgrades: Capacity expansion
Roundabout Practice Locations for New Drivers
Beginner-Friendly Roundabouts:
- Dubai Silicon Oasis residential roundabouts: Low traffic, clear markings
- Sports City roundabouts: Good visibility, predictable traffic patterns
- Jumeirah Village Circle: Multiple small roundabouts for practice
Intermediate Challenge:
- Al Barsha roundabouts: Moderate traffic, good for timing practice
- Business Bay roundabouts: More lanes, business traffic patterns
- JLT (Jumeirah Lake Towers) roundabouts: Pedestrian interaction practice
Advanced Mastery:
- Defense Roundabout: Peak hour navigation
- Mirdif roundabouts: Complex multi-exit navigation
- Deira commercial area roundabouts: High-density, unpredictable traffic
Roundabout Navigation for Special Vehicles
Large Vehicles (Trucks, Buses):
- Wider turns: Need more space
- Multiple lanes: Sometimes permitted to use two lanes
- Patience required: They accelerate and stop slower
Motorcycles and Bicycles:
- Positioning: Often between lanes (filtering)
- Visibility: Harder to see, especially in blind spots
- Right-of-way: Same as cars when in lane
Emergency Vehicles:
- Rule: Must yield and create path
- Technique: Move to right without blocking their intended direction
- Don’t: Stop in middle of roundabout unless necessary
The Psychology of Roundabout Success
Building Confidence:
- Start small: Practice at quiet roundabouts first
- Passenger guidance: Have experienced driver observe initially
- Timing practice: Visit same roundabout at different times of day
- Exit mastery: Perfect your signaling and exit technique
Managing Anxiety:
- Breathing technique: Deep breaths when approaching
- Positive self-talk: “I know the rules, I can do this”
- Alternative routes: Have backup plans for particularly stressful roundabouts
- Practice during low-traffic hours: Early Sunday mornings are ideal
Common Roundabout Myths Debunked
Myth 1: “You must always signal left when entering”
Truth: No signal required when entering. This actually confuses other drivers.
Myth 2: “The largest vehicle has right-of-way”
Truth: Right-of-way belongs to vehicles already in roundabout, regardless of size.
Myth 3: “Roundabouts are faster than traffic lights”
Truth: In low-to-moderate traffic, yes. In heavy traffic, sometimes signals are more efficient.
Myth 4: “You can change lanes anywhere in the roundabout”
Truth: Only when safe and necessary, with proper signaling.
Myth 5: “Emergency vehicles always enter roundabouts with lights/sirens”
Truth: They must still exercise caution and may not always use audible signals in roundabouts.
Roundabout Accident Procedure
If You’re Involved in an Accident:
- Move to safety if vehicles are drivable (exit roundabout completely if possible)
- Call police (999) if there are injuries or significant damage
- Exchange information if minor (license, registration, insurance)
- Use Dubai Police app for minor accident reporting
- Do not argue about fault at the scene
Determining Fault:
- Primary factor: Who failed to yield?
- Secondary factor: Who was in which lane?
- Evidence: Dashcam footage is extremely valuable
- Witnesses: Get contact information if available
Technology Aids for Roundabout Navigation
In-Vehicle Assistance:
- GPS warnings: Some systems alert about roundabouts ahead
- Lane guidance: Premium systems show which lane to use
- Heads-up displays: Keep eyes on road while getting guidance
Mobile Applications:
- Google Maps/Waze: Show roundabout layout and lane guidance
- Dubai Police App: Report incidents, check fines
- Drive Mode Apps: Minimize distractions during navigation
Dashcams:
- Front-facing: Capture entry and circulating actions
- Rear-facing: Capture following vehicles’ behavior
- Dual-channel: Both angles for complete coverage
Roundabout Rules for Specific Dubai Communities
School Zones:
- Increased caution during drop-off/pick-up times
- Watch for school buses stopping unexpectedly
- Patience with student drivers in academic areas
Industrial Areas (JAFZA, DIP):
- Large vehicle awareness: Trucks have limited visibility
- Shift change timing: Increased traffic at specific hours
- Road conditions: Sometimes poorer maintenance
Tourist Areas (Downtown, Marina):
- Rental cars: Drivers may be unfamiliar with roundabouts
- Pedestrian density: Higher, especially evenings
- Alternative routes: Often available if roundabout is congested
The Future of Roundabouts in Dubai
Trend Analysis:
- Gradual replacement: With controlled intersections
- Smart technology integration: Adaptive control systems
- Safety improvements: Better lighting, signage, and markings
- Capacity enhancements: Additional lanes where possible
Driver Education Initiatives:
- RTA awareness campaigns: Focus on yielding and lane discipline
- Driving school curriculum: Enhanced roundabout training
- Expat orientation: Including roundabout rules in relocation packages
Your Personal Roundabout Improvement Plan
Week 1: Knowledge Foundation
- Memorize the four critical steps
- Study the fine structure
- Identify challenging roundabouts on your regular routes
Week 2: Observation Practice
- Be a passenger and observe other drivers
- Note common mistakes and near-misses
- Practice predicting other drivers’ actions
Week 3: Controlled Practice
- Practice at low-traffic roundabouts early mornings
- Focus on one skill at a time (entry timing, lane discipline, exiting)
- Record yourself or have experienced driver provide feedback
Week 4: Real-World Application
- Navigate your most challenging regular roundabouts
- Practice during moderate traffic conditions
- Build confidence through repeated success
Ongoing: Continuous Improvement
- Adjust for weather conditions
- Stay updated on rule changes
- Share knowledge with family and colleagues
Conclusion: Mastering Dubai’s Roundabouts
Navigating Dubai roundabout rules successfully requires more than just memorizing regulations—it demands situational awareness, defensive driving skills, and psychological preparedness. The roundabout is a microcosm of Dubai’s driving environment: diverse, dynamic, and demanding attention to detail.
Remember that every roundabout presents an opportunity to practice patience, precision, and predictability—three qualities that define excellent driving anywhere in the world. The confidence gained from mastering Dubai’s roundabouts extends to all aspects of driving, making you a safer, more competent driver on every road.
As Dubai continues to evolve its infrastructure, roundabouts may gradually give way to other intersection designs. But for now, they remain a critical component of the city’s road network. Your mastery of them not only keeps you safe and fine-free but contributes to the smooth flow of traffic that makes Dubai’s remarkable mobility possible.
Approach each roundabout not as an obstacle, but as an opportunity to demonstrate your driving competence. With the knowledge from this guide, you’re equipped to navigate Dubai’s roundabouts with confidence, safety, and skill.